Este blogue é destinado aos estudantes, professores e os interessados em aprender um pouco de Língua Estrangeira Moderna, o Inglês.
Translate
sexta-feira, 11 de abril de 2014
quinta-feira, 10 de abril de 2014
DAILY ROUTINE

Common verbs to describe Daily Routine:
wake up – wash your face – do morning exercise – take a shower – watch morning news on TV – dry your hair – brush your teeth – eat breakfast – brush your teeth – get dressed – go to the bathroom – make your bed – go to school – go to work – study – have lunch – get home – do your homework – have dinner – take a bath – go to bed – go to sleep.
Now let’s look at the following reading and conversation! People are talking about daily routine. Then practice to talk about that in English
Reading activities about Daily Routine
Pre-reading questions
- What’s your job?
- What do you do in your free time?
- How do you spend your day?
- Do you get up early on weekends
Read the passage and conversation , answer the questions below:
Daily Routine
 My name’s Christine Yang. I am from China. I am a university student. I study Economics. I get up very early at around 6.30 every weekdays. I do morning exercise in about 30 minites. I have breakfast at 7.00 am. I go to school at 7.30 because my classes start at 8.00 am. I finish school at 11.30, and I have lunch at school cafe. I leave school at 4.00 in the afternoon. I arrive home at 4.30 pm. I have dinner at 6 and then watch T.V or go on the internet for a while. I learn my lesson and prepare for coming class till 11.00 pm and I go to bed.
My name’s Christine Yang. I am from China. I am a university student. I study Economics. I get up very early at around 6.30 every weekdays. I do morning exercise in about 30 minites. I have breakfast at 7.00 am. I go to school at 7.30 because my classes start at 8.00 am. I finish school at 11.30, and I have lunch at school cafe. I leave school at 4.00 in the afternoon. I arrive home at 4.30 pm. I have dinner at 6 and then watch T.V or go on the internet for a while. I learn my lesson and prepare for coming class till 11.00 pm and I go to bed.
Questions:
- What does Yang do?
- What time does she get up on weekdays?
- what does she do before having breakfast?
- What time does she leave home?
- Where does she have lunch?
Conversation 1: Daily Schedules
- Kim: What do you do every day, Bob?
- Bob: I get up at about 10.00 on weekdays.
Then I watch News on T.V for an hour and have breakfast at about noon. - Kim: Really? What time do you go to work? .
- Bob: I start work at 4.00 pm.
- Kim: And what time do you arrive home at night?
- Bob: I get home quite late, at midnight.
- Kim: What do you do exactly?
- Bob: Well, I am an……..
Questions:
- What time does Bob get up?
- What time does he have lunch?
- What time does he start work?
- When does he arrive home at night?
http://englishonlinecenter.com/2011/11/learning-to-talk-about-daily-routines-in-english/
PRESENT PERFECT AND PAST SIMPLE
Can you use the present perfect and the past simple? Have a look at this cartoon and explain the difference to your partner.
Look at the signal words to distinguish both tenses:
In this link you have more practice:
http://www.englishpage.com/verbpage/verbs5.htm
http://2esobilingualnorba.blogspot.com.br/
terça-feira, 18 de março de 2014
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
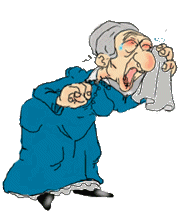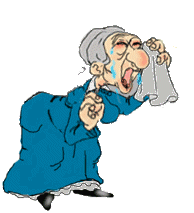
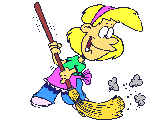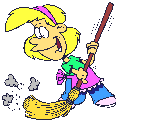
Look at the pictures and write about what it is happening.
Use the following verbs: do homework/ travel/ play/ dance/ cry/ rain/ clean house/ fly plane/carry suitcases/hunt/ eat/ wave/cycle or ride bike/ open/sleep/ deliver mail/investigate/ run/ walk dog/ paint fence/ drink coffee
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
http://www.englishexercises.org/makeagame/viewgame.asp?id=6819
PRESENT SIMPLE OR PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Use the Present Continuous with Normal Verbs to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment.
Spelling of Verb + ING
For many verbs we make the ING form by simply adding -ING to end of the verb.
- eat – eating
- speak – speaking
- cook – cooking
- start – starting
- do – doing
- stay – staying
- fix – fixing
- try – trying
Verbs ending with -e (with the exception of verbs ending in -ee and -ie)
Drop the -e and add ING
- hope – hoping
- ride – riding
- make – making
- write – writing
Verbs ending with -ee
Just add -ING
- agree – agreeing
- flee – fleeing
- see – seeing
Verbs ending with -ie
Change the -ie to -y and add -ING
- die – dying
- tie – tying
- lie – lying
Verbs ending with one vowel and one consonant (with the exception of w, x, and y)
For one syllable verbs
double the consonant and add -ING
- jog – jogging
- sit – sitting
- run – running
- stop – stopping
For two syllable verbs
If the 1st syllable is stressed, just add ING
- answer – answering
- offer – offering
- listen – listening
- visit – visiting
If the 2nd syllable is stressed , double the consonant and add ING
- admit – admitting
- prefer – preferring
- begin – begining
NOW, THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE PRESENT SIMPLE AND PRESENT CONTINUOUS IS, PRESENT SIMPLE IS FOR ROUTINES, THINGS THAT YOU ALWAYS, USUALLY, SOMETIMES DO, WITH A FREQUENCY OF TIME, THAT IS WHY THE ADVERB OF FREQUENCY GOES WITH PRESENT SIMPLE.
THEN, PRESENT CONTINUOUS IS AN ACTION I DO RIGHT NOW, AT A PERIOD OF TIME, AND AFTER THAT, IT ENDS.
http://englishteacherdotme.wordpress.com/tag/present-simple-or-present-continuous/
domingo, 16 de março de 2014
quinta-feira, 13 de março de 2014
Future will
Professora Andréa: Future tense - will: FUTURE WITH WILL Futuro – expressa ações que irão acontecer. O futuro simples é formado pelo auxiliar WILL seguido do verbo principal no ...
terça-feira, 25 de fevereiro de 2014
Have to / Has to
HAVE TO / HAS TO Remember· “Have to” is used to express obligation (when something is necessary).
Ex. I have to make my bed everyday 
· Have to is used with I, you, we, they (in affirmative sentences)
Fill in the gaps using “have to”, “has to”, “don’t have to”, “doesn’t have to”
- We get up early on Mondays

- Mary go to school on Saturdays
- She wear glasses because she can’t see very well

- John tidy his bedroom before going to bed.
- I lay the table before having lunch

- You take your math book to school today, you don’t have math class

- He wear uniform in his school. Everybody can wear what they like.
- My father is a policeman. He wear a uniform.

Say whether these sentences are in present or past
- We didn’t have to get up early last Saturday
- She has to go to school
- Did you have to set the table?
- We have to visit our grandparents
- He had to tidy his room yesterday





segunda-feira, 24 de fevereiro de 2014
domingo, 23 de fevereiro de 2014
What is Mickey Mouse doing?

https://www.blendspace.com/lessons/m1Yw4XMN65aQDQ/present-simple-versus-present-continuous
Countries & nationalities - Worksheet
Teaching-Frenzy: Countries & nationalities - Worksheet: Hello there! I'm back to work and back to my Worksheets as well. This one is about personal information and it was developed for begi...
Assinar:
Postagens (Atom)








